What is it?
Understanding skin cancer is the first part to effective treatment and prevention.
- Most common type of cancer
- Can be self-diagnosed from symptoms but should be examined by a doctor
- Treatable by a medical professional
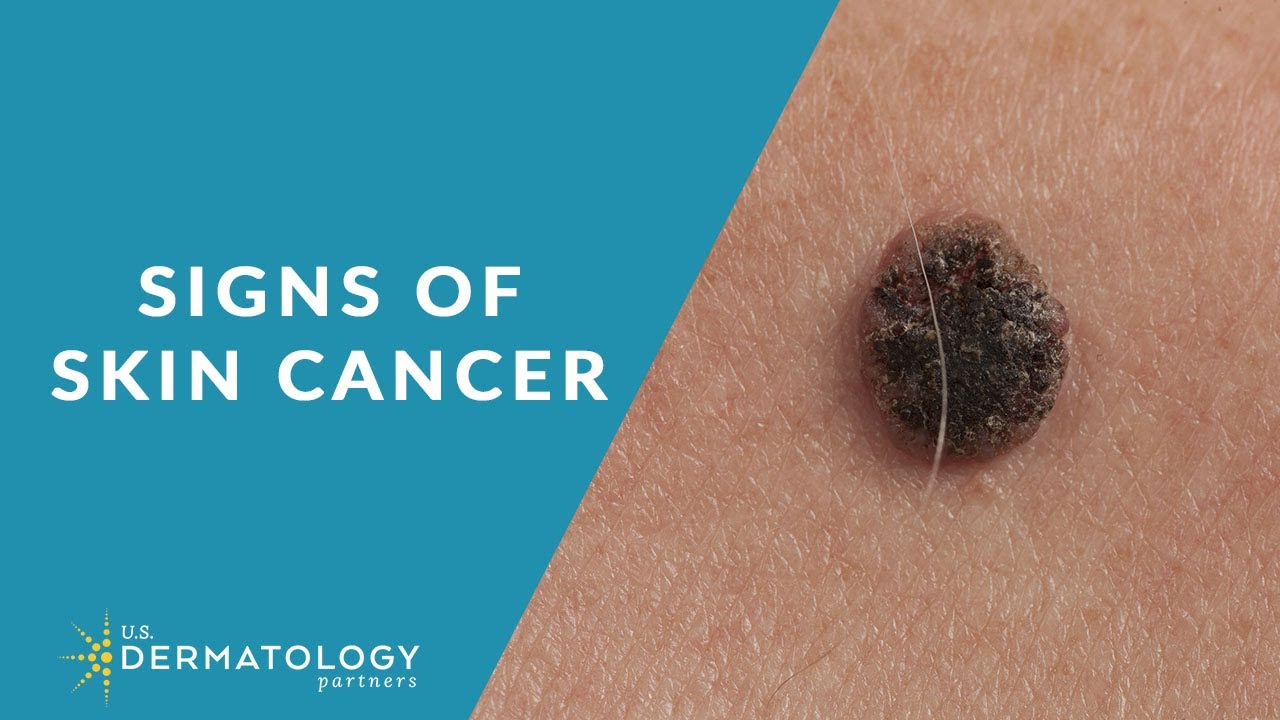
Skin cancer is a skin injury caused by mutations occurring in the skin cell DNA which cause abnormal cells to multiply out of control. One of the most common causes of these DNA mutations leading to skin cancers are UV radiation, which is found in sunlight and tanning lamps/beds. Although too much UV radiation increases your risk of skin cancer, not spending enough time in the sun can also increase the risk of skin cancer, especially those who are genetically predisposed or have weakened immune systems. The symptoms that develop are determined by the type and severity of the skin cancer. However, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) tend to have small blood vessels visible within the tumor and a central depression with crusting/bleeding (ulceration). Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) commonly has a well-defined, red, scaling, thickened bump on sun-exposed skin that could ulcerate and bleed. Abnormal brown or pink spots and moles are another common symptom. There's no specific cure for skin cancers, but there are available treatment options. The most common treatment is surgery such as wide excision, lymphatic mapping, lymph node dissection, radiation therapy usually with around a 92% Success Rate. On the other hand, medication is also used such as immunotherapy (25-45% success rate), targeted therapy, and chemotherapy (12-15% success rate).
You Can Prevent Skin Cancer
There are many ways to reduce the chances of sustaining skin cancer. See prevention tips listed below.
- Slip on some sun-protective clothing that covers as much skin as possible
- Put broad spectrum water-resistant SPF30 sunscreen or higher
- Wear a hat, or appropriate protection to your face and head
- Seek shade
- Wear Sunglasses, that meet appropriate standards
Find out more about how Dasion diagnoses skin cancer.
Upload your EEG data to our service and receive accurate diagnoses immediately.
Existing Diagnosis Models:
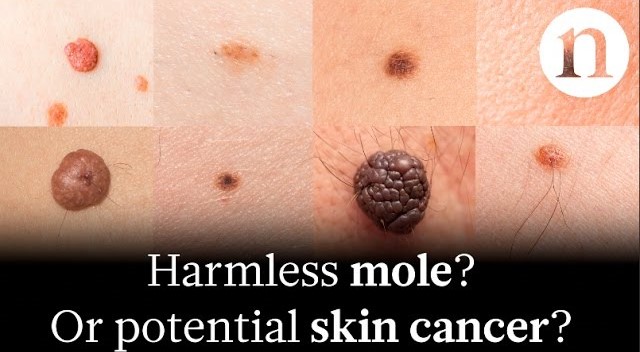
What does Skin Cancer look like?
Find out if you may have sustained Skin Cacner.
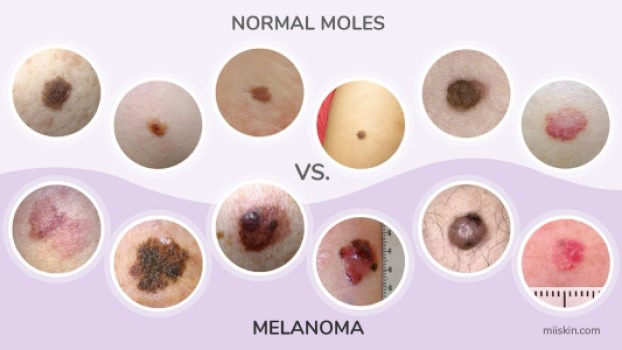
Melanoma (skin cancer) is diagnosed by the 'ABCDE' rule after continual exposure to UV radiation:
- Asymmetry: an asymmetrical mole
- Border: a mole with an uneven border
- Color: a mole with two or more colors
- Diameter: moles larger than 5 mm
- Elevation: a mole that is becoming raised
- Firm: a mole that feels firm
- Growing: a mole that shows signs of changes
Note: While these signs from the ABCDE rule is usually sufficient for a diagnosis of skin cancer, it is not necessary.